Polarimetric imaging for quality control in injection molding
I presented a work on the use of polarimetry for injection molding quality control at the SPIE QCAV2019 conference, in Mulhouse, France. The associate paper can be found here. The venue was great, fitted my research, with rich talks and offline discussions.
I met other PhD students which were using non-conventional imaging for original purposes, and also private startup researchers on quality control with deep learning.
This work use the low cost polarimeter I built last summer. It is possible to acquire degree and angle of polarimetry with a 1080p resolution.
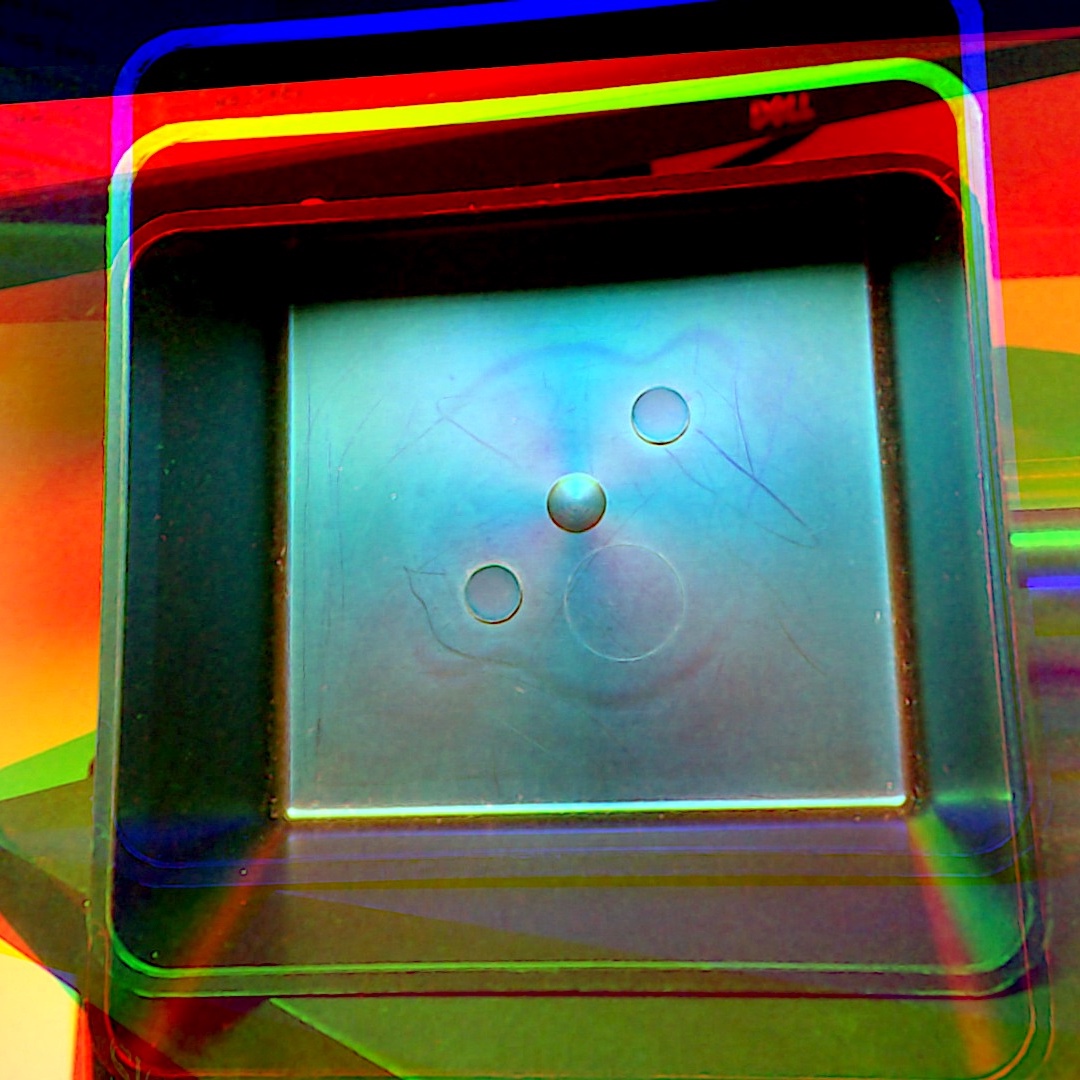
It is also possible to reconstruct the first three Stokes parameters from the linear polarization of light. Then, it is possible to separate diffuse from specular reflections.
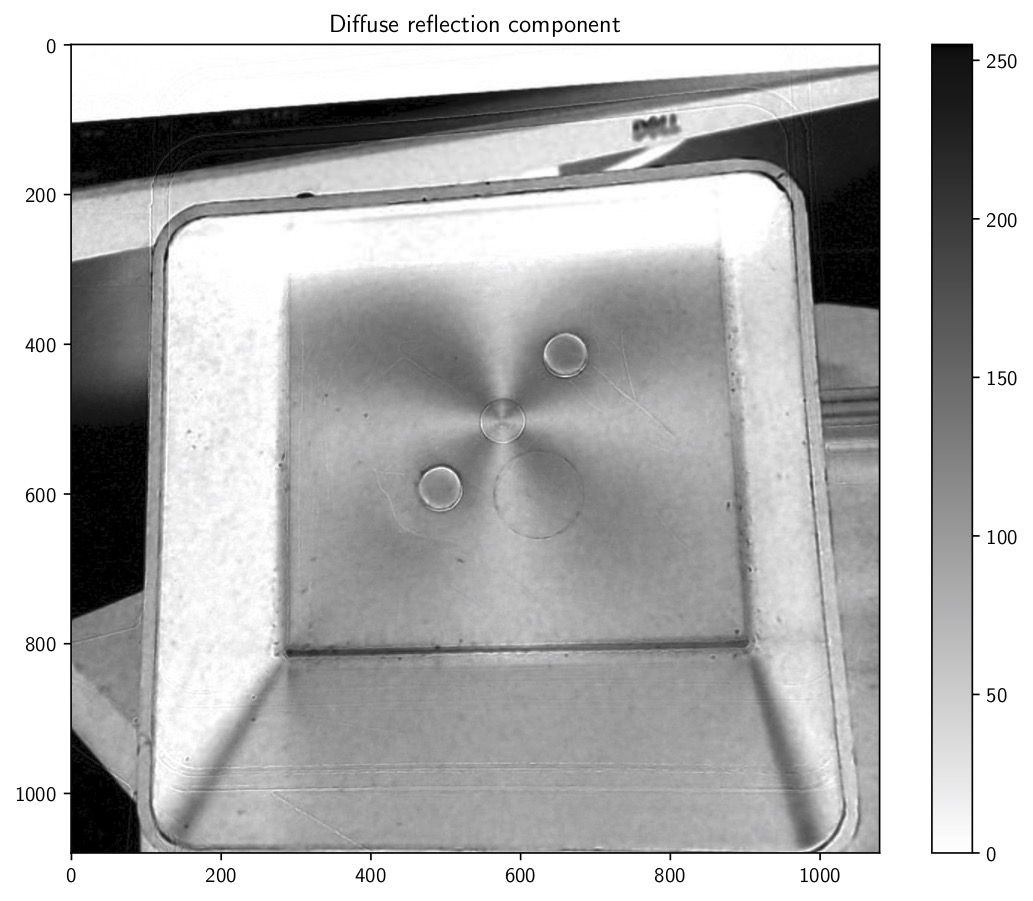
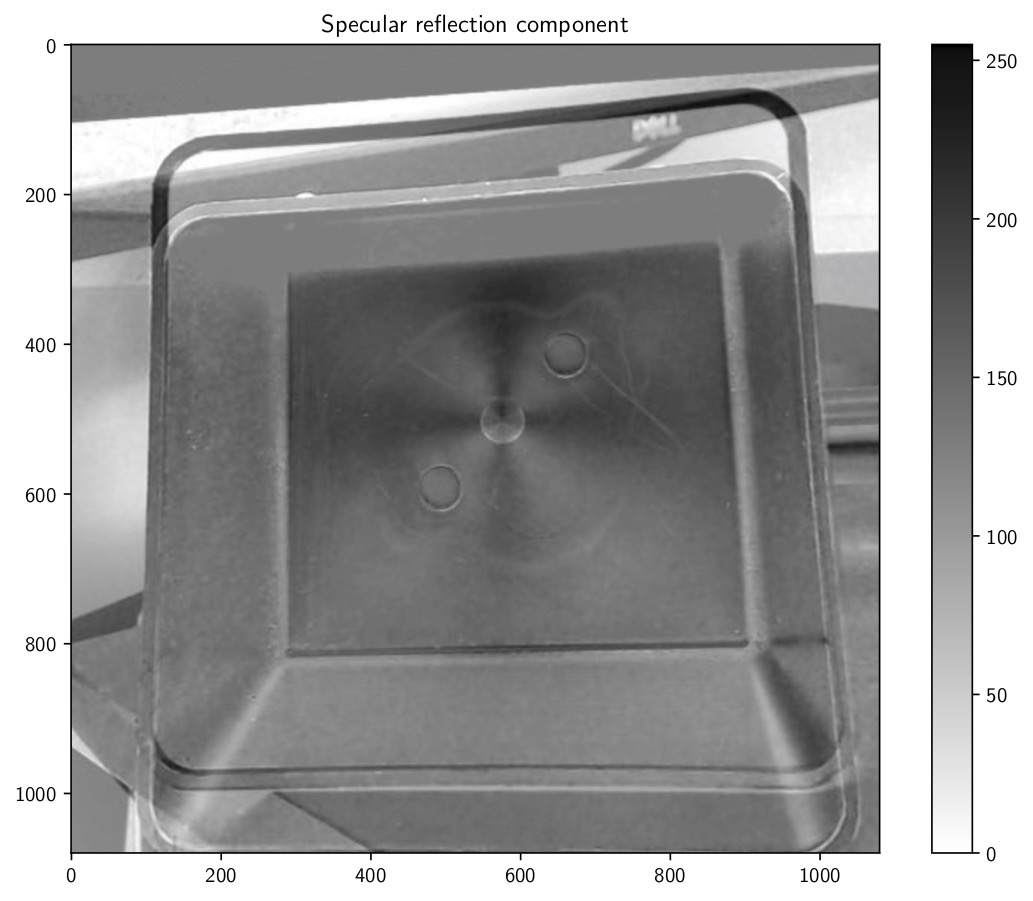
To find if polarimetry helps to detect defects, I propose the use of a machine learning pipeline for binary classification: part is ok or defective. The training dataset have a hundred part, which is small in comparison with litterature standards.
I propose a dataset with the same part captured with three different capture modalities. With or without linearly polarized light and with or without polarized camera. The objective is to find which modality gives the best defect classification score.
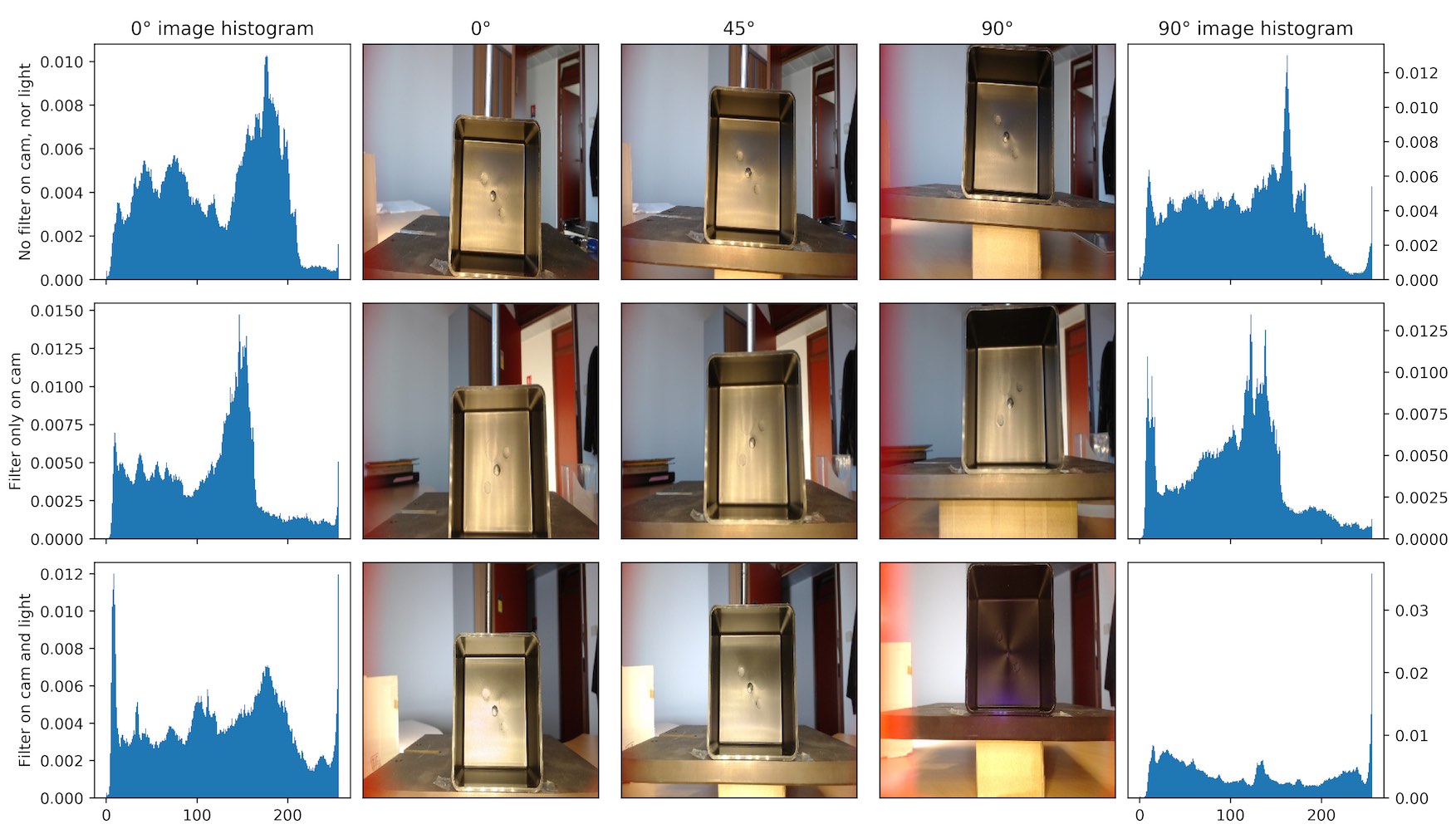

To avoid machine learning pipeline bias, for each case, I found the best pipeline using genetic optimization with the TPOT library.
| Camera polarized filter angle | Light polarized | Light not polarized | Benchmark without light nor polarized cameras |
|---|---|---|---|
| All 3 cameras with 3 angles | 0.876 | 0.876 | 0.948 |
| 0° polarized camera | 0.820 | 0.875 | 0.923 |
| 45° polarized camera | 0.820 | 0.769 | 0.820 |
| 90° polarized camera | 0.846 | 0.820 | 0.889 |
Results are promising, but it show that polarimetry is less important that having three different viewpoints.




